
Gravity die casting is a cornerstone manufacturing process renowned for producing high-quality metal components with precision and efficiency. In the article, we delve into the fundamentals of this technique, exploring its advantages, applications, and the expertise that Moldiecasting brings to the table.
What is Gravity Die Casting?
Gravity die casting is a method where you can create detailed metal parts by using a metal mold and the natural force of gravity. This process gives you an excellent surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
In gravity die casting, molten metal is simply poured into a permanent mold without force. The molten metal fills the mold cavity using gravity alone. Here are the basic steps:
- Prepare the mold: The mold, which is usually made of steel, is heated and then coated to prevent the metal from sticking.
- Melt the metal: Alloys such as aluminum, copper, zinc, and magnesiumare melted into a liquid form.
- Pouring: The molten metal is poured into the mold cavity.
- Cooling: Once inside the mold, the metal cools and begins the solidification
- Ejection: After the metal has solidified, the part is removed from the mold.
After gravity die casting, your cast parts will likely require additional steps to meet the exact standards for surface finish and precision. Let’s explore how machining, surface treatments, and inspections play a crucial role in delivering high-quality castings.
Once you take your casting out of the die, machining is often required to achieve the final shape and dimensions. CNC machining is a precise way to remove any excess material, especially from areas like the parting line. This level of precision ensures that your casting meets the necessary dimensional accuracy and repeatability for the desired application.
Surface treatments and coatings are applied to achieve an excellent surface finish and enhance strength. Your castings may undergo processes such as:
- Polishing: To smooth out the surface for a high-quality look and feel.
- Sandblasting: To clean and texture the surface, removing any impurities.
- Painting or die coating: To protect the metal and improve its resistance against environmental factors.
Materials for Gravity Die Casting
Non-ferrous alloys are commonly used for gravity die casting. Here’s a list of metals and their properties that you might choose:
- Aluminum: Lightweight, strong, and resistant to corrosion.
- Copper Alloys: Known for their electrical and thermal conductivity.
- Zinc: Offers high strength and hardness.
- Magnesium: Extremely light with a high strength-to-weight ratio.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gravity Die Casting

Gravity die casting offers a balance of design flexibility and performance for creating metal parts. Whether you’re in automotive, aerospace, or consumer goods, this process might be what you need.
High-Quality Surface Finish: You’ll get a smoother surface right out of the mold, reducing the need for extensive finishing work. The process allows for high dimensional accuracy, which means the parts you make will fit together well and function as intended.
- Cost-Effective: Especially for medium to high volume production runs, gravity die casting is a cost-effective method. Tooling costs are usually lower compared to other casting processes, and it provides a greater rate of production with fewer defects.
- Design Flexibility: You have the freedom to create complex shapes and intricate designs with gravity die casting that other methods may not permit. Coupled with high strengthmaterials, your parts can meet the rigorous demands of various industries without compromising on aesthetics.
- Accuracy: If your components require precise measurements and tight tolerances, you’ll find gravity die casting can achieve that consistency.
Gravity die casting, despite its widespread use, presents several notable disadvantages. One major drawback is its significant design limitations, as the process relies solely on gravitational forces for metal flow, making it difficult to produce complex geometries, thin walls, and parts with undercuts.
Technical limitations further compound these issues, as gravity die casting is best suited for smaller aluminum and zinc alloy components and struggles with larger parts due to potential deformation.
Quality concerns, including susceptibility to defects like cold shuts and misruns, as well as longer production lead times, make this method less ideal for projects that demand precision and rapid turnaround.
Applications of Gravity Die Casting Parts
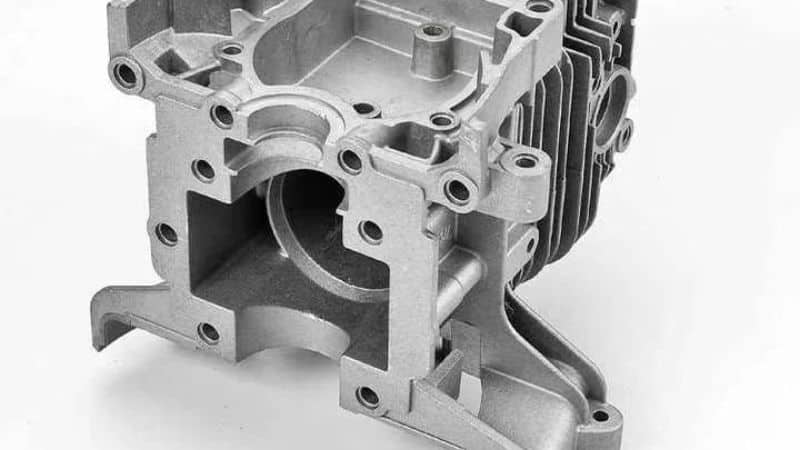
Industrial Machinery: Your machines need parts that can withstand tough conditions. Gravity die casting facilitates the manufacturing of durable engine blocks and other components that are integral to industrial machinery.
- Automotive Parts: Whether it’s gearboxes or chassis components, gravity die casting is widely used in the automotive industry because of its ability to produce strong and lightweight parts which can enhance vehicle performance and safety.
Aerospace Components: In aerospace, every gram counts. Gravity die casting helps create components that not only meet strict regulatory standards but also contribute to the overall weight reduction and efficiency of aircraft.
- Consumer Goods: On a more everyday level, this casting process is behind some of the durable goods you use around your home. From kitchen appliances to electronic enclosures, gravity casting makes products last longer.
Compared Gravity Die Casting with Other Casting Methods
| Process Type | Key Strengths | Main Limitations | Best Applications |
| Gravity Die Casting | – Good surface quality
– Moderate tooling cost – Simple equipment needs |
– Limited to simple designs
– Slower cycle times – Size restrictions |
– Automotive parts
– Industrial components – Kitchen equipment |
| Sand Casting | – Low setup cost
– Any metal possible – Large parts feasible |
– Rough surface finish
– Lower accuracy – Labor intensive |
– Heavy machinery
– Large components – Prototypes |
| Low-Pressure Die Casting | – Better fill control
– Less porosity – Good for thin walls |
– Higher equipment cost
– Limited material options – Complex setup |
– Engine blocks
– Wheel rims – Complex parts |
| High-Pressure Die Casting | – Excellent detail
– Fast cycles – Thin walls possible |
– Very high tooling cost
– Size limitations – Material restrictions |
– Electronics housings
– Small components – High volume parts |
| Investment Casting | – Highest precision
– Complex geometries – Excellent finish |
– Most expensive process
– Slow production – Small parts only |
– Aerospace parts
– Medical devices – Jewelry |
Partner With Moldiecasting
For high-quality metal casting solutions, Moldiecasting offers exceptional die casting services that deliver outstanding results.
For projects requiring precise specifications and reliable performance, Moldiecasting stands as your trusted partner. With years of dedicated experience in gravity die casting, Moldiecasting specializes in delivering superior casting solutions across various industries.
If you’re looking for professional die casting services that combine technical expertise with customer-focused solutions, don’t hesitate to contact Moldiecasting for your casting requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does gravity die casting compare to pressure die casting?
While both involve molten metal and molds, gravity die casting uses the force of gravity, resulting in slower fill times and potentially less turbulence within the molten metal. Pressure die casting, on the other hand, uses high pressure to force metal into the mold, leading to faster production rates and finer details in the casting.
What is the minimum wall thickness achievable in gravity die casting?
The minimum wall thickness in gravity die casting can be quite thin, but a general threshold is around 3 mm, which allows for adequate flow of molten metal and solidification without defects. Design considerations must be balanced with the physical properties of the metal and the complexity of the part.
