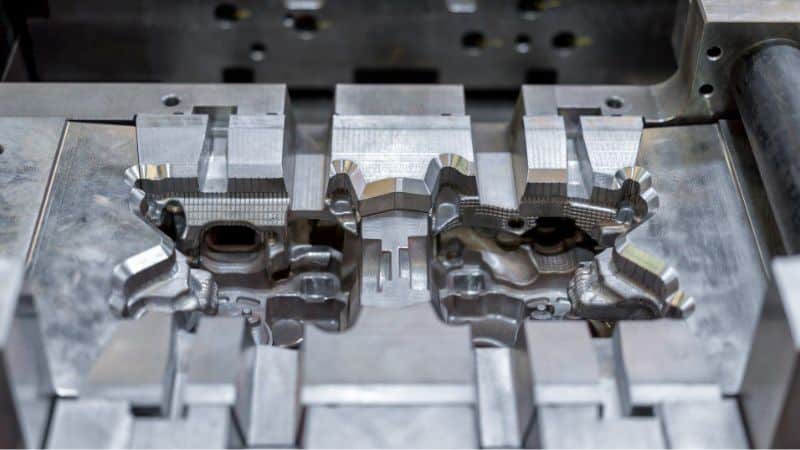

Die casting and sand casting are the two most widely used casting methods.
This article explores the key differences between die casting and sand casting, examining factors such as production volume, part complexity, wall thickness, cost-effectiveness, and material properties.
What is Die Casting?
In die casting, metal is melted and injected under high pressure into a metal mold, also known as a die. The molds used in die casting are usually made from steel and can withstand high temperatures, which allows for a quicker manufacturing process compared to sand casting. Mold cavity surfaces are designed to create intricate parts with a high level of detail. This reusable mold feature leads to a more consistent finish in your products.
Here’s a basic outline of your die casting process:
- Prepare the Die: Clean and coat with a release agent.
- Clamp the Die: Securely close the two halves of the mold.
- Inject Molten Metal: The molten metal is forced into the die cavity under high pressure.
- Cooling: The metal solidifies into the desired shape.
- Eject: Open the die and remove the casting.
What is Sand Casting?
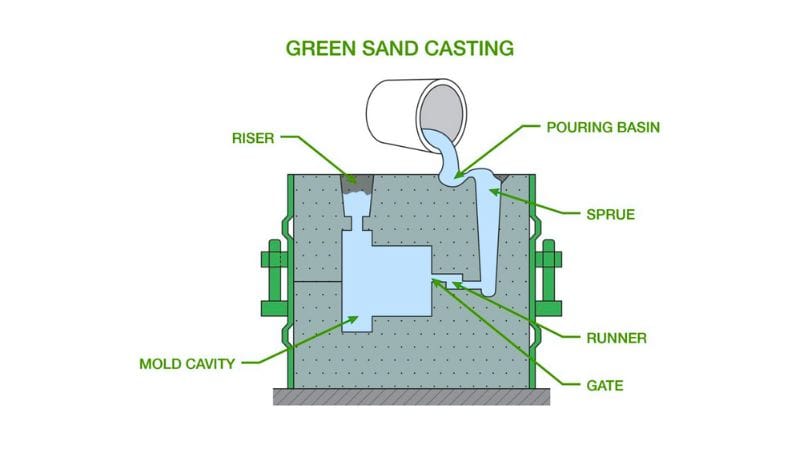
Sand casting, in contrast to die casting, uses a mold made from sand to shape your metal parts. This method is versatile because it can handle metals with a high melting point and large parts. It’s one of the oldest and most traditional forms of casting, known for its flexibility in materials and shapes.
After the metal is poured into the mold and solidified, the sand mold is broken to remove the casting. Unlike the robust metal molds in die casting, sand molds are only used once, which can result in slight variations in each cast and a rougher surface finish. However, sand casting has a lower start-up cost and is adaptable to a wide range of metals.
For sand casting, the sand casting process typically involves:
- Creating the Mold: Pack sand around a pattern of your part.
- Remove the Pattern: Once the sand is compacted, you remove the pattern, leaving a cavity.
- Pour Molten Metal: Pour the molten metal into the sand mold’s cavity.
- Solidification: Give time for the metal to cool and harden.
- Break Away Mold: Break the sand mold to reveal the rough casting.
- Finishing: Clean and finish the casting as needed.
Differences Between Sand Casting and Die Casting?
Here is a chart for you to have a glance at the differences:
| Criteria | Sand Casting | Die Casting |
| Mold Material | ● Iron (both cast and wrought): Great for heavy-duty components.
● Brass: It’s a go-to for good corrosion resistance. ● Bronze: Offers excellent wear resistance. |
● Zinc: This is the easiest metal to cast; it offers high ductility and high impact strength and is the most economical for small parts.
● Aluminum: Known for its lightweight nature, it’s also very strong and can withstand high temperatures. ● Magnesium: If you need something super lightweight yet sturdy, this is your pick. |
| Surface Finish | Rougher finish | Smoother finish |
| Production Efficiency | Lower efficiency | Higher efficiency |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Dimensional Accuracy | Less accurate | More accurate |
| Versatility | Very versatile | Less versatile |
Pros and Cons of Die Casting and Sand Casting
Pros of Die Casting:
- Better dimensional accuracy
- Faster production rates for high-volume needs
- Smooth surface finishes
Cons of Die Casting:
- Higher initial setup costs for molds
- Restricted to metals with lower melting points
- Less suitable for large or highly intricate parts
Pros of Sand Casting:

- Lower initial costs for mold setup
- Ability to cast large and complex parts
- More material options, including high melting point metals
Cons of Sand Casting:
- Rougher surface finish
- Lower dimensional accuracy
- Slower production rate for individual items
How to Choose Between Die Casting and Sand Casting?
If your project requires high precision and faster production rates, and you are looking to manufacture a large volume of small to medium-sized components, die casting is likely the better option. Conversely, if you need flexibility for larger parts or are working with lower volumes where cost-effectiveness is crucial, sand casting may be more suitable.
| Factor | Die Casting | Sand Casting |
| Production Volume | Best for high-volume production | Suitable for low to medium-volume production |
| Part Complexity | Excels at complex parts with intricate geometries | More flexible for larger and simpler designs |
| Wall Thickness | Capable of producing thinner walls | Typically results in thicker walls |
| Surface Finish | Produces excellent surface finishes | Results in rougher surface finishes |
| Cost Considerations | Higher initial tooling costs, cost-effective for high volumes | Lower initial costs, but may incur higher overall expenses |
| Material Properties | Stronger and more durable parts due to pressure | Versatile with various alloys, but may have lower durability |
Applications of Die Casting and Sand Casting Parts
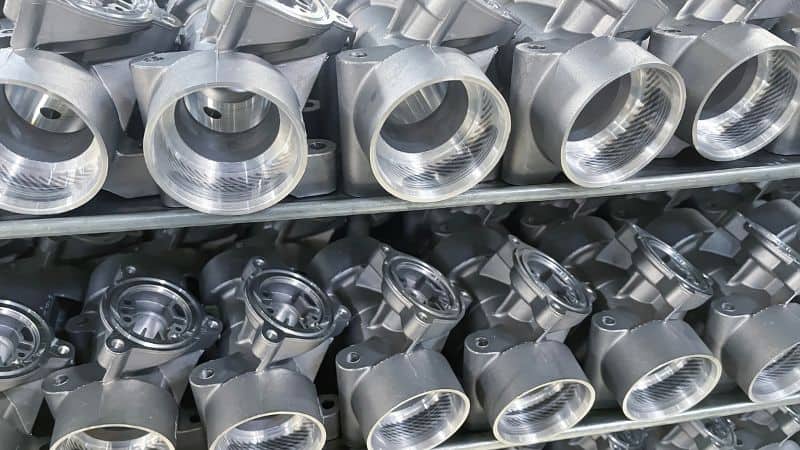

| Casting Method | Industry | Applications | Examples of Products |
| Die Casting | Automotive | Manufacturing engine components, transmission parts | Aluminum alloy engine blocks, structural components |
| Consumer Electronics | Lightweight and intricately designed components | Smartphone cases, laptop shells | |
| Telecommunication | Components for telecommunications equipment | Antenna housings, connectors | |
| Aerospace | High-quality, lightweight components | Aircraft housings, turbine blades | |
| Medical Devices | Instrument casings and device components | Precision-machined aluminum parts | |
| Sand Casting | Heavy Machinery | Large and heavy machinery components | Iron engine blocks, gears, pulleys |
| Architectural | Decorative and ornamental metalwork | Gates, railings, sculptures | |
| Art and Craft | Unique metal sculptures and artistic pieces | Bronze sculptures | |
| Power Generation | Manufacturing turbine blades and casings | Steel turbine blades | |
| Marine | Components for marine applications | Brass marine fittings, propellers |
Your Next Project With Moldie Casting
Embarking on your next project with Moldie Casting means partnering with a team of experienced engineers dedicated to delivering high-quality die casting solutions tailored to your needs.
Our commitment to quality is reinforced by rigorous testing and analysis throughout the mold production process, ensuring durability and low maintenance.
With advanced technology and a focus on customer satisfaction, Moldie Casting is ready to bring your vision to life—contact us today to discuss how we can support your next project!
