Automotive die casting is a process used to make strong, lightweight metal parts for cars quickly and accurately. This method shapes metals like aluminum by forcing them into molds at high pressure, creating parts like engine blocks, transmission cases, and wheels.
Understanding how die casting works helps explain why it is so common in modern car factories. It saves time, reduces waste, and produces parts that fit together well, improving both car safety and performance. People interested in cars, manufacturing, or engineering can learn a lot from seeing how die casting shapes the vehicles on the road today.
Overview of Automotive Die Casting
Automotive die casting is used to manufacture strong and lightweight metal parts for cars and trucks. This process supports fast production while keeping quality and consistency high.
Definition and Fundamentals
Automotive die casting is a process where molten metal is injected under high pressure into a steel mold. This method creates parts with precise shapes and smooth surfaces. The die casting process is popular for making various car components. The process can be produce parts over and over with tight tolerances. and also reduces wasted material compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
Role in the Automotive Industry

Die casting is a major technique for making auto parts because it guarantees strength and light weight properties. Parts produced by the technique help reduce a vehicle’s total weight, which improves fuel efficiency and lowers emissions.
Automotive die casting supports mass production and keeps costs down. It also helps manufacturers meet strict safety and quality standards needed in the automotive industry.
Material Selection and Applications
Material selection in automotive die casting affects part weight, durability, and manufacturing costs. Metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium each have important roles based on their distinct properties and the needs of different automotive parts.
Choosing Suitable Metals
Automotive die casting uses metals with specific properties that meet the demands of the auto industry. The three main metals are aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. Each of these is suited to different parts and requirements.
Aluminum die casting is the most commonly used in cars. It is chosen for engine blocks, transmission cases, and wheels because it is lightweight and strong. Zinc die casting is popular for smaller parts like locks and handles due to its fine detail and smooth finish.
Magnesium die casting stands out for its low weight. This metal is chosen for parts where reducing weight is very important. Choosing the right metal depends on cost, required strength, and where the part will be used.
| Metal | Common Uses | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | Engine blocks, wheels, housings | Lightweight, strong |
| Zinc | Handles, locks, brackets | Fine detail, smooth |
| Magnesium | Dashboards, supports, housings | Very light, easy to cast |
Benefits of Aluminum, Zinc, and Magnesium
Aluminum die casting provides a good balance between weight and strength. It resists corrosion, does not rust easily, and has good thermal conductivity. Aluminum die-casting is best for parts that must be light but still strong.
Zinc die casting allows for very precise shapes and thin walls. It helps create parts with detailed features. Zinc also has high impact strength. This makes it useful where both strength and good surface detail are important.
Magnesium die casting offers the lightest weight among the three. It is often used where reducing the overall mass of the car is a major goal. Magnesium parts are easy to machine and assemble. However, they are less strong than aluminum, so engineers use them mainly for covers, supports, and housings.
Die Casting Processes in Automotive Manufacturing
Die casting in the automotive industry uses several methods to shape complex metal parts with accuracy. Each process has unique features, equipment, and materials best suited for different vehicle components and production needs.
High Pressure Die Casting
High pressure die casting is one of the most common die casting processes used in automotive manufacturing. In this method, molten metal is injected into a steel mold under very high pressure, often between 1,500 and 25,000 psi. This helps produce parts with precise details and smooth surfaces.
Key advantages include fast cycle times and high output, which are important for producing parts like engine blocks and transmission housings. The process also works well with alloys such as aluminum and magnesium, which are common in lightweight cars.
Despite its benefits, high pressure die casting can result in trapped air inside the part, which may affect strength.
Low-Pressure Die Casting
Low-pressure die casting works by forcing molten metal into a mold using lower pressure, usually below 1,000 psi. The metal is introduced from below, rising gently into the die. This method is slower than high pressure die casting but allows for better control over the filling process.
This process is often used to make wheels, suspension components, and larger structural parts that require a dense, strong structure with fewer air pockets.
Advantages of this method include:
- Producing parts with good mechanical properties
- Less risk of gas porosity
- Greater consistency in wall thickness
Low-pressure die casting can use both aluminum and magnesium alloys, making it a flexible choice for many applications.
Hot Chamber Die Casting
Hot chamber die casting uses a process where the injection system sits inside the molten metal bath, which is then drawn straight into the chamber and injected into the die quickly.
This process is mainly suited for metals with lower melting points, such as zinc, magnesium, and some lead alloys. It is not used for aluminum alloys, which would damage the injection system.
Hot chamber die casting is ideal for automotive parts that are small, thin, and need high-volume production. Parts like brackets, connectors, and small housings are good fits.
Key points include:
- High speed
- Low cycle time
- Good finish
- Limited to specific metal types
Cold Chamber Die Casting
In cold chamber die casting, molten metal is poured manually or automatically into the injection chamber, which is separate from the melting furnace. A piston then forces the metal into the die under high pressure.
This method is designed for metals with higher melting points, such as aluminum, brass, and copper alloys. The separation keeps these metals from damaging the injection system, unlike in hot chamber methods.
Cold chamber die casting is widely used in automotive manufacturing for parts like engine blocks, transmission cases, and wheels. The process allows for larger parts and produces strong components with intricate designs.
Notable features are:
- Slower cycle time compared to hot chamber
- Can handle larger parts
- Suitable for a broader range of alloys
- Essential for high-strength automotive parts
Key Automotive Components Produced by Die Casting
Automotive die casting is widely used to produce precise metal parts. Common products include engine parts, transmission housings, and structural supports for vehicle frames.
Engine Blocks and Cylinder Heads

Die casting allows for complex shapes needed in engine blocks and cylinder heads. Aluminum is often used for these parts because it keeps the engine light and strong. Engine blocks made from die casting help engines cool better and last longer.
Cylinder heads produced by die casting can include intricate passages for air, fuel, and coolant. This improves engine efficiency and reduces waste. The precise tolerances available with die casting help reduce leaks and improve performance.
These benefits make die-cast engine blocks and cylinder heads important in modern cars.
Transmission and Gearbox Housings
Transmission housings and gearboxes are essential for moving power from the engine to the wheels. Die casting is used to make these parts fit tightly and handle heating and vibrations. This process produces thin walls and smooth surfaces, which are both important for ideal operation.
Using die casting, factories can create transmissions with complex outer shapes that include mounting points and fluid passages. This reduces the need for extra assembly steps or fixing errors. Lower part weight also means less energy needed to drive the vehicle.
Chassis and Structural Components
Chassis parts and structural supports made with die casting include items like engine mounts, crossmembers, and subframes. These parts need to be strong but not too heavy. Die casting lets manufacturers add ribs and other features to reinforce parts without adding weight.
Structural components must meet strict safety rules. Die casting helps ensure parts are formed with consistent quality. This makes it easier for car makers to assemble frames that are both safe and cost-effective.
Example components made by die casting:
- Engine mounts
- Suspension parts
- Crossmembers
- Subframes
These die-cast parts keep vehicles strong, stable, and safe during use.
Advantages of Automotive Die Casting
Automotive die casting lets manufacturers use lightweight metals to create strong yet thin parts. This helps improve weight reduction, lower fuel consumption rate, and supports environmentally friendly design in modern vehicles.
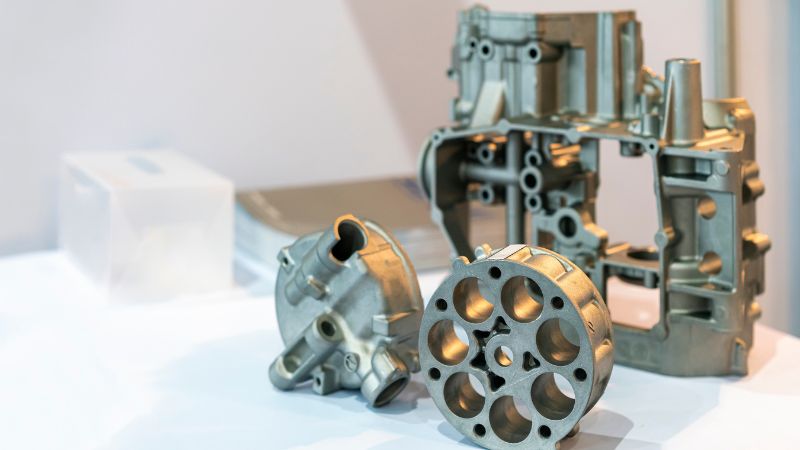
Lightweight Components and Weight Reduction
Die casting is well known for its use of lightweight metals, such as aluminum and magnesium. These materials make it possible to produce car parts that weigh much less than traditional steel components.
Benefits of lightweight die cast components:
- Lower overall vehicle weight
- Improved acceleration and braking
- Easier assembly and maintenance
- Reduced stress on tires and suspension
Weight reduction is a big goal in car manufacturing, because it can lead to better handling and faster acceleration. Lighter parts also mean automakers can meet strict rules for vehicle safety without sacrificing performance or durability.
Fuel Efficiency and Environmental Impact
Weight reduction achieved by die casting directly helps with fuel efficiency. Lighter vehicles need less fuel to move, which improves their miles per gallon ratio. This is especially important as fuel economy standards become stricter across the world.
Reduced fuel use means fewer greenhouse gas emissions. This supports environmental friendliness and helps manufacturers follow environmental rules more easily. Better fuel economy also lowers fuel costs for drivers and reduces the use of natural resources.
Automotive die casting can help create more energy-efficient and lightweight automobiles. This is a key reason it remains a popular choice for engineers and car makers trying to design greener vehicles.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does the die casting production process differ from investment casting in automotive applications?
Die casting uses high pressure to force molten materials into a metal mold. Investment casting uses a wax pattern and ceramic mold and is done at lower pressures. Die casting is faster and better for making many identical parts.
How does the die casting production process impact the durability of automotive parts?
Die cast parts are known for their consistent strength and good resistance to wear. However, the process can introduce small air pockets, which may affect some parts if not controlled. Improved methods continue to address these issues.
What are the latest advancements in die casting technology for the automotive industry?
Recent improvements include better mold materials and more precise control of temperature and pressure. Some factories use automated robots for faster and more accurate production. Advances in alloys are helping make parts even lighter and stronger.
