Automated die casting service, as a manufacturing method, is the fruit of advanced modern technologies, managing the casting process with less manual work and better quality control.
As factories move toward smart manufacturing, this method plays an important role for manufacturers like Moldie. In this blog, we will present to you how automation benefits your projects with better products and lower costs.
How Automation Transforms the Die Casting Process & Quality
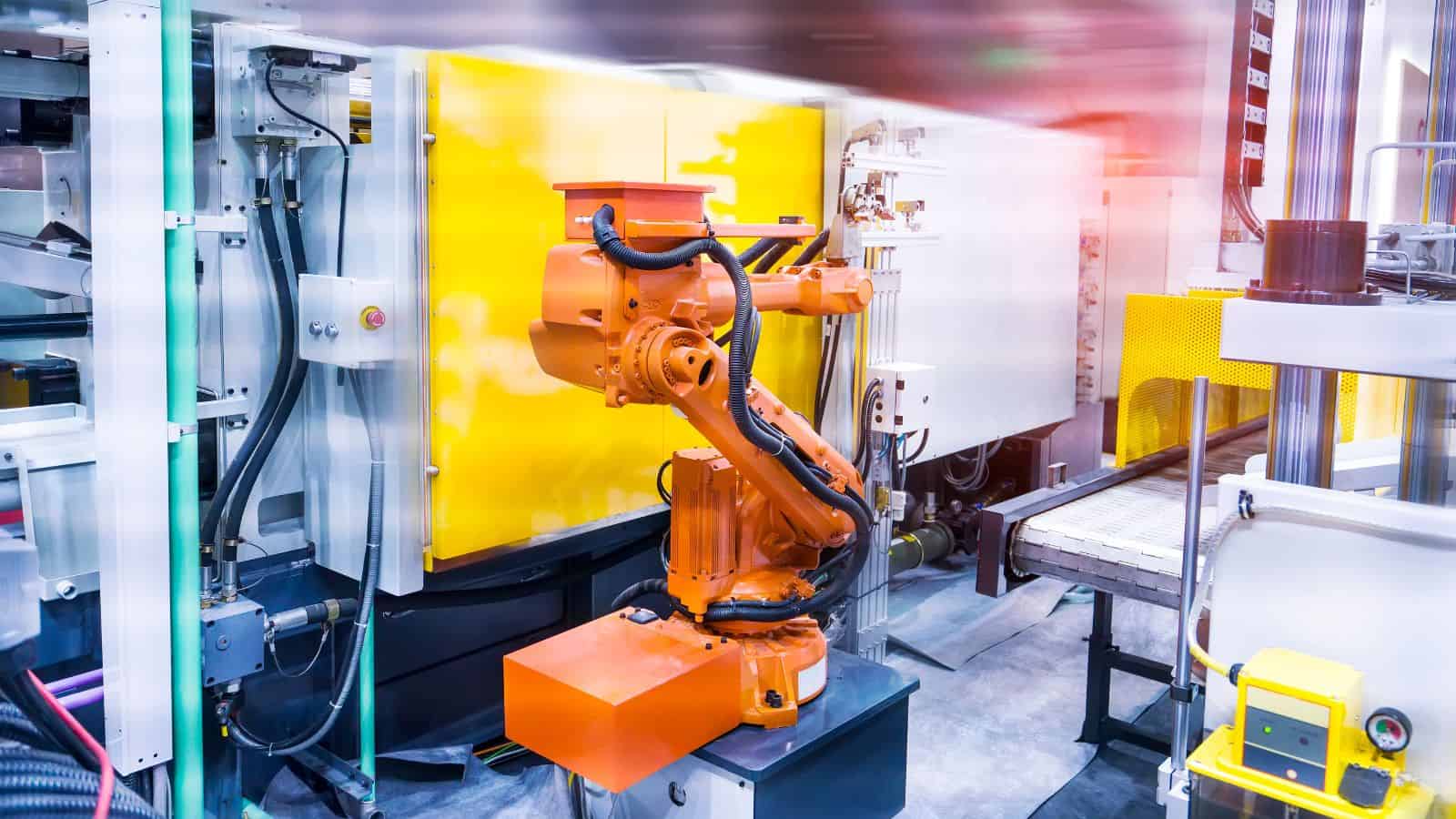

Automated die casting replaces many manual tasks with controlled systems. This reduces variation caused by human timing and handling.
Sensors track temperature, pressure, and cycle time during each shot, and the machine adjusts settings when values drift from targets.
Key changes introduced by automation include:
- Consistent cycle timing across shifts
- Early defect detection through vision and sensors
- Lower scrap rates from stable process control
Types of Die Casting Machines Used in Automation
Automation systems vary between specific die casting machine types. Each type is built in different ways based on its mechanisms and material choices.
| Machine Type | Common Use | Why It Fits Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Chamber | Aluminum, magnesium | Handles high melt temperatures with robotic ladling |
| Hot Chamber | Zinc, low-melt alloys | Faster cycles and easier full-cell automation |
| Vertical Die Casting | Inserts, small parts | Precise insert loading with robots |
Modern casting machines often include PLC controls, servo drives, and data links. These features allow integration with robots, conveyors, and inspection systems.
Core Components of Automated Die Casting Systems
Automated die casting systems rely on precise motion control, coordinated equipment, and reliable finishing steps. These elements work together to move molten metal, handle hot castings, and deliver consistent parts at high volumes.
Robotic Handling and Material Feeding
Robotic material handling manages the most demanding tasks, including casting parts, placing them on cooling stations, and transferring them to the next step without delay.
Material feeding systems support steady production. Automated ladles or feeders deliver molten metal at a set volume and speed. This accuracy helps control part weight and reduces scrap.
Key functions often include:
- Part extraction from the die
- Automated ladling of molten metal
- Controlled cooling and part transfer
Integration of Peripheral Devices
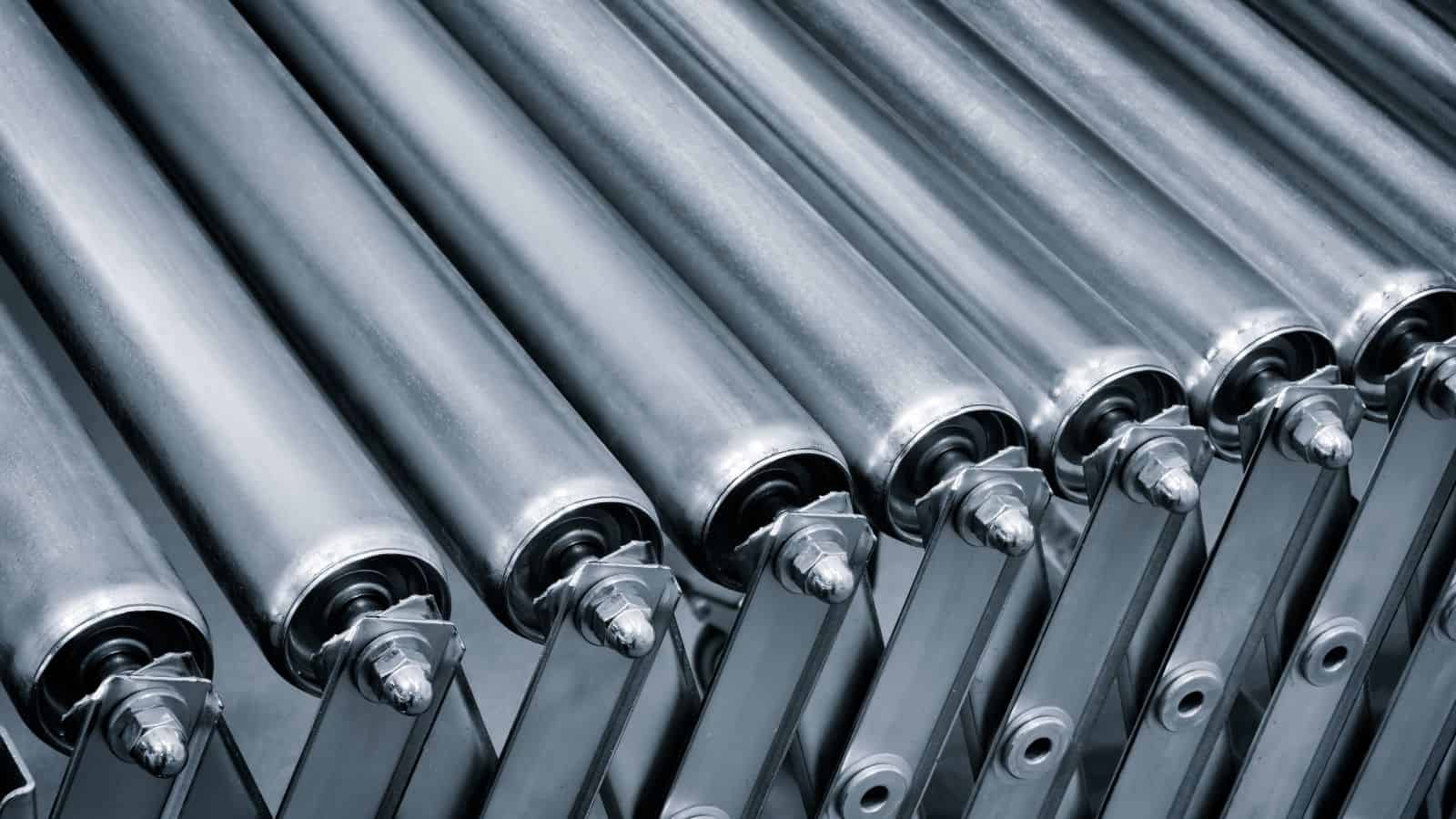

Peripheral devices extend automation beyond the casting machine. These devices include mold spray units, cooling conveyors, sensors, and inspection tools. Integration allows them to share data and act in sequence.
Central control systems link each device. They track production status, part counts, and alarms in real time. Operators can see clear production data on a single interface.
Common integrated devices include:
| Device | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Mold spray unit | Applies even release and cooling spray |
| Cooling conveyor | Lowers part temperature safely |
| Sensors and vision | Check part presence and defects |
This coordination reduces manual steps and keeps quality stable.
Trim Press and Deburring Automation
Trim press automation removes excess metal from cast parts with speed and accuracy. Robots load and unload trim presses, which cut gates and flash in a single stroke. This setup keeps parts aligned and protects tooling.
Deburring automation follows trimming, which removes sharp edges using brushes, cutters, or blasting media. Automated handling ensures each part receives the same treatment.
Advantages of automated trimming and deburring include:
- Consistent edge quality
- Lower labor demand
- Reduced part damage
These systems help deliver clean, ready-to-use components without slowing production.
High Quality and Consistency of Automated Die Casting
Automated die casting improves part accuracy by controlling key process variables, reducing defects, and keeping production stable over long runs. These systems also support workplace safety by limiting manual work near hot equipment.
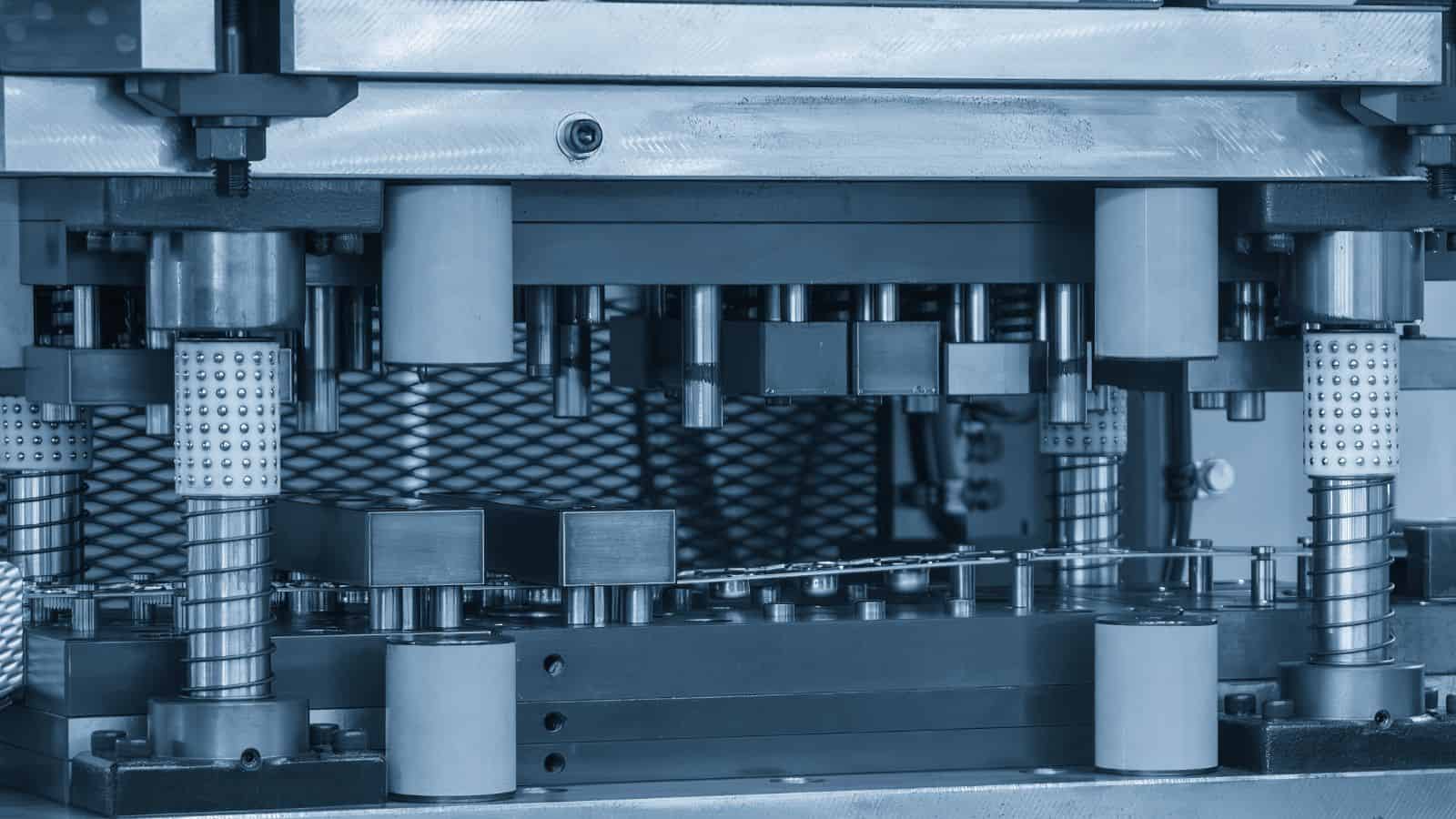
Process Control and Monitoring
Automated systems keep tight control over the process, which directly affects casting quality. Sensors track these values during every shot and send data to a central system. The system adjusts settings in real time to keep conditions within set limits.
Operators use dashboards to view live data and spot trends early. This reduces variation between parts and across shifts. Consistent settings also protect the die from excess wear, which helps maintain part dimensions.
Common monitored parameters include:
- Melt temperature
- Injection speed and pressure
- Die temperature
- Cooling time
Stable process control lowers scrap rates and supports repeatable results at scale.
Defect Detection and Prevention
Automated defect detection focuses on finding problems as early as possible. Machine vision systems inspect parts for surface defects such as cracks, misruns, or flash. Some systems also flag signs of internal issues linked to porosity or shrinkage.
AI-based software compares each part to known quality standards. When the system detects a deviation, it alerts operators or stops the line. This prevents large batches of defective parts.
Continuous Flow Manufacturing
Continuous flow manufacturing keeps parts moving through the production process of metal feeding, part removal, and transfer with minimal stops.
A stable flow reduces temperature swings and timing errors. These issues often cause defects in manual or stop-start operations. Automation also improves consistency between cavities and across long production runs.
Key benefits of continuous flow include:
- Shorter and more stable cycle times
- Uniform part quality
- Lower operator exposure to heat and motion
This approach supports high casting quality while creating a safer and more controlled production environment.
Production Efficiency and Cost Reduction with Automated Die Casting
Automated die casting improves output speed, controls material use, and lowers operating expenses. It supports large production volumes while managing energy use and scrap in a more controlled way.
Mass Production Capabilities
Automated die casting service pairs best with high-volume mass production for its stable cycle times. Robots repeat the same actions with tight control, which keeps part dimensions consistent from one shot to the next.
Manufacturers reduce delays by linking all components into one line. Parts move from casting to trimming and inspection without waiting for manual handling.
Key production benefits include:
- Shorter cycle times due to fast and repeatable motions
- Higher uptime with fewer interruptions
- Consistent part quality across large batches
This setup works well for automotive, industrial, and electronics parts that require thousands or millions of identical components.
Reducing Manufacturing and Energy Costs
Automation helps reduce manufacturing costs by lowering labor needs and limiting rework. Robots pour metal, spray dies, and remove parts with precise control, which cuts defects caused by variation.
Material use becomes more predictable. Accurate ladling reduces excess metal, which lowers scrap rates and post-processing work.
Energy costs also drop in several ways:
- Faster cycles reduce run time per part
- Automated systems limit idle time between shots
- Aluminum die casting uses less energy than many alternative processes
Together, these factors reduce cost per unit while keeping output stable at scale.
How Automation Influences Recycling
Automation improves recycling efficiency by keeping scrap clean and separated. Robots collect runners, flash, and rejected parts without mixing them with oils or debris.
Clean scrap returns directly to the melting process. This reduces the need for new raw material and lowers energy use during remelting.
Automated inspection also plays a role. Systems detect defects early and remove faulty parts before added value steps like machining or coating.
Recycling benefits from automation include:
- Higher reuse rates of aluminum
- Lower material waste per batch
- More stable melt quality
These practices support cost control while reducing material loss in daily production.
Smart Manufacturing and Innovations
Automated die casting now relies on data, sensors, and software as much as machines. Smart manufacturing links equipment, people, and systems to cut downtime, raise quality, and allow faster decisions across the plant.

Predictive Maintenance and AI Integration
Predictive maintenance uses sensor data to spot wear, track heat, pressure, vibration, as well as cycle time. AI models review this data and flag risks early.
Plants replace parts based on condition, not fixed schedules. This approach cuts unplanned stops and lowers spare part costs. It also extends die life and improves uptime.
Common inputs for AI systems include:
- Die temperature and cooling flow
- Injection speed and pressure
- Lubrication timing
- Motor load and vibration
AI also adjusts process settings during runs. It fine-tunes shot speed or cooling to keep results stable. These actions support smart manufacturing by keeping machines productive with less manual control.
Quality Assurance in Smart Die Casting
Smart die casting shifts quality checks from end-of-line to real time. Sensors inside the die track fill and pressure during each shot. Systems compare results to known good ranges.
Inline inspection tools add another layer of control. Plants use X-ray or CT scans with robots to check parts without slowing output. Software logs each result to support traceability.
Key quality controls and their roles
| Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Cavity pressure sensors | Confirm full and even fill |
| Thermal cameras | Detect hot spots and cooling issues |
| Inline X-ray | Find porosity and cracks |
| Data logs | Support audits and root cause review |
These tools reduce scrap and rework. They also help teams correct issues during production, not after.
Digitalization and Remote Monitoring
Digitalization connects machines, tools, and planning systems. Dashboards show live status for output, scrap, and energy use. Managers see issues as they form.
Remote monitoring allows teams to act without being on the floor. Engineers review alarms, trends, and videos from secure systems. This setup supports faster response and safer operations.
Common digital features include:
- Live machine dashboards
- Cloud-based data storage
- Remote alarms and alerts
- Production and energy reports
Digital twins add more value in some plants. They simulate production runs using real data. Teams test changes before applying them, which reduces risk and speeds setup.
